
Botox is a popular migraine treatment. It blocks the action of Acetylcholine, which is a chemical that causes muscle contractions. Although the treatment is not suitable for all, many have reported a reduction in pain or even complete elimination. This treatment is increasingly popular with migraine sufferers. Botox can reduce pain and is relatively safe with very few side effects.
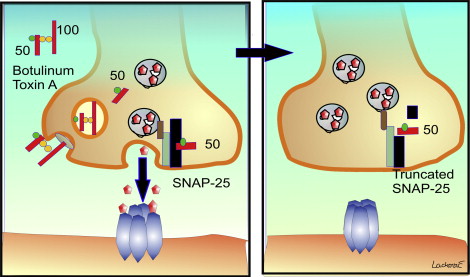
Botox inhibits the release Acetylcholine
Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholines in the brain, which are responsible for pain signals. This stops migraines from happening by preventing abnormal muscle contractions and stiffness. It is safe, effective and painless for treating migraines.
It involves injecting Botox into the area using tiny needles. The procedure takes just a few minutes, and the patient can do it while sitting or lying down. Botox, unlike regular injections, does not penetrate deeply into the muscles.
It reduces muscle contractions
Botox is an injectable medication that can be used to treat chronic migraines. The FDA approved drug contains purified Botulinum Toxin. It relaxes muscles and decreases headache frequency. Usually, Botox is given in minute doses to treat migraines. Patients are given an anesthetic cream and lotion during the procedure.
Certain types of muscle spasticity can also be treated with the drug. This disorder causes muscles contract involuntarily. It can also be a sign of a neurological disorder or stroke. Spasticity is something that approximately twenty-three percent to thirty percent stroke survivors will experience.
It is safe
Botox is a neurotoxin made by the Clostridium botulinums bacteria, and when given incorrectly, can cause a dangerous reaction called botulism. The toxin works by blocking nerve signals and paralyzing the muscles. Because the toxin doesn't pass through the stomach it can be safely used. It cannot also be absorbed into the bloodstream. This treatment can be used to treat a wide range of conditions including spasms and tics as well as wrinkles.
It is possible to experience allergic reactions, though it is uncommon. Rarely, allergic reactions to the toxin can lead to difficulty swallowing or swelling of the legs. These symptoms aren't serious enough to forbid Botox treatment. To avoid this reaction, patients should read the Botox allergy warning.
This is only for chronic migraine sufferers.
Botox can only be purchased on the NHS by those suffering from chronic migraines. Clostridium botulinum makes the drug. Although it was originally developed to treat eye conditions, the drug has been used for many other conditions, including migraine. The Department of Health has approved its NICE appraisal.
Although they may not be suitable for all patients with chronic migraines, injections can still be used for those who have exhausted other options. Bash and Migraine Trust endorse the NHS's use of it and believe it should also be available to all those who are eligible. According to the NHS website chronic migraine patients should be able receive Botox injections in case they fail to manage their condition with preventative medicine.